IoT Fundamentals and Applications
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects devices embedded with sensors, software, and network capabilities to communicate and exchange data.
This interconnected system automates and enhances various aspects of daily life by enabling devices to operate intelligently and interact seamlessly.
IoT’s impact spans multiple areas, transforming environments through data-driven automation and user-centric control interfaces.
Definition and core components of IoT
IoT consists of devices equipped with sensors, connectivity, and software to collect and share data, enabling intelligent interactions.
Core components include smart devices, communication networks, data processing units, and user interfaces that facilitate monitoring and control.
Connections are often wireless, using protocols like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth to enable real-time data exchange for automated and optimized operations.
Primary IoT application areas
Key IoT applications include smart homes, wearables for health tracking, and various connected devices in domestic and industrial settings.
Smart homes use IoT to automate lighting, security, and energy management for enhanced comfort and efficiency.
Wearables monitor health metrics, while connected devices improve safety, productivity, and convenience across diverse environments.
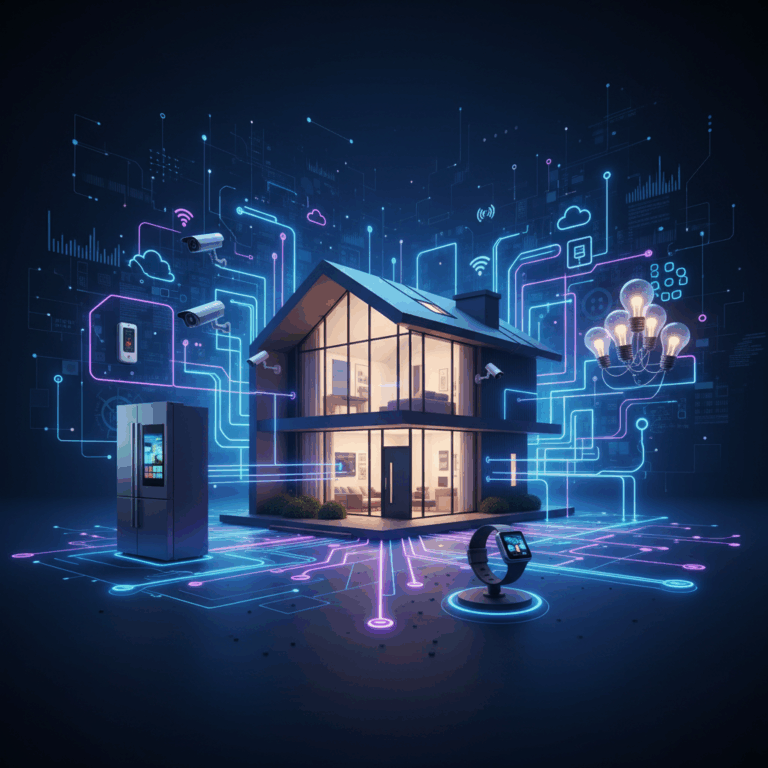
Smart Homes and Their Features
Smart homes utilize IoT technology to create intelligent living spaces where devices communicate and coordinate actions.
These homes feature interconnected sensors and appliances that enhance comfort, security, and energy use through automation.
Connectivity and advanced protocols enable seamless device interaction, transforming everyday life with convenience and safety.
Interconnected devices and communication protocols
Smart homes rely on various communication protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave for device connectivity.
Devices such as thermostats, lighting, and cameras connect via these protocols, forming a network that enables real-time data sharing.
A central hub often coordinates the data flow, allowing devices to work in harmony for automated responses.
These protocols ensure secure and efficient communication while supporting diverse device types and manufacturers.
Automation, security, and energy efficiency
Automation in smart homes enables tasks like adjusting lighting or temperature based on sensor data or user schedules.
Security systems use cameras, motion sensors, and alerts to provide real-time monitoring and protection tailored to residents’ needs.
Energy efficiency is optimized by controlling appliances and systems, reducing unnecessary consumption, and lowering utility costs.
These features collectively create safer, more sustainable, and responsive home environments.
User interaction through apps and voice assistants
Smart home devices are controlled through intuitive apps and voice assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant.
This interaction allows users to monitor and manage their homes remotely with simple commands or automation routines.
Voice control increases accessibility and convenience, creating seamless communication between users and connected devices.
Enhancing daily living through intuitive control
By integrating apps and voice technology, smart homes offer personalized experiences, adapting to user preferences effortlessly.
Wearables and Health Monitoring
Wearable devices are IoT gadgets worn on the body that monitor health and fitness in real-time, enhancing personal well-being and connectivity.
These devices track various metrics such as heart rate, steps, and sleep, providing users with valuable insights about their health status continuously.
Beyond individual use, wearables also play a significant role in workplace safety by monitoring vital signs and alerting users to potential hazards.
Types and functionalities of wearable devices
Wearables include smartwatches, fitness trackers, smart glasses, and medical devices, each offering unique features tailored to different needs.
Common functionalities cover activity tracking, heart rate monitoring, GPS navigation, and notifications, ensuring users stay informed and active.
Many wearables integrate advanced sensors that detect physiological signals, aiding in early health issue detection and improved fitness management.
Connectivity options like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi enable seamless data synchronization with smartphones and cloud services for comprehensive monitoring.
Health tracking and workplace safety applications
Wearables provide continuous monitoring of vital signs, detecting irregularities in heart rate or activity that indicate potential health concerns.
In workplaces, devices track environmental hazards and worker conditions, helping prevent accidents and improve overall safety.
Real-time alerts from wearables allow prompt response to emergencies, making them valuable tools for both personal health and occupational safety.
These applications contribute to improved productivity, reduced risks, and better management of employee well-being in various industries.
Connected Devices and Emerging Technologies
The IoT ecosystem includes a wide variety of connected devices designed to improve efficiency and convenience in many environments.
These devices gather and analyze data to automate everyday tasks, enhancing safety, comfort, and productivity in homes and industries.
Emerging technologies further expand IoT capabilities, enabling more sophisticated interactions among diverse devices.
Variety and roles of connected devices
Connected devices range from smart kitchen appliances to industrial sensors, all linked to collect real-time information and optimize functions.
Each device plays a specific role, from monitoring environmental conditions to controlling automated processes for user benefit.
These gadgets work together within networks to create smart systems that respond dynamically to changing needs and situations.
Advances in wireless technologies and interoperability
Recent developments in wireless communication, such as LoRa and Matter protocols, improve range, security, and device compatibility.
Interoperability standards enable diverse devices to communicate smoothly, fostering a cohesive and secure IoT environment.
These advances support scalability and integration, ensuring future IoT systems remain flexible and user-centric.